
Introduction: In the digital era, the safeguarding of personal information has become paramount. This section delves into the methodologies that prioritize the protection of sensitive data from the inception of technological solutions. By embedding these safeguards early in the development process, we aim to create a robust framework that inherently respects user confidentiality.
Strategic Integration: The approach discussed here involves a thoughtful integration of security measures at every stage of product development. This proactive strategy not only enhances the trustworthiness of digital offerings but also ensures compliance with evolving regulations. It is a shift from reactive measures to a more preventive stance, aiming to mitigate risks before they materialize.
Through this exploration, we will uncover how such an integrated approach can lead to more resilient and user-centric digital products. The focus is on creating a seamless experience that does not compromise on the essential aspect of data integrity and user autonomy.
Understanding Privacy by Design
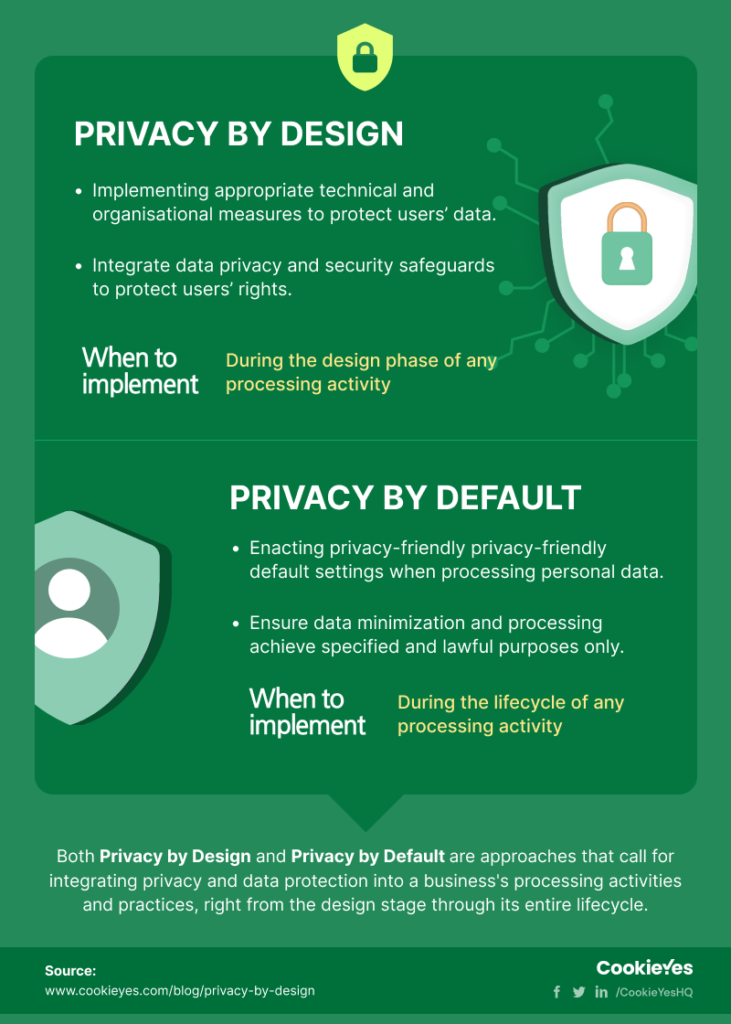
This section delves into the critical role of early integration of confidentiality safeguards in the development process. It emphasizes the necessity of incorporating these protections from the inception of a project to ensure robust security measures are in place throughout the lifecycle of the product or service.
Early integration of confidentiality safeguards is pivotal for several reasons:
- Enhanced User Trust: By prioritizing confidentiality from the outset, organizations demonstrate a commitment to protecting user data, which can significantly enhance user trust and loyalty.
- Compliance and Legal Benefits: Early implementation helps align products and services with evolving regulatory requirements, potentially avoiding costly retrofits and legal issues.
- Operational Efficiency: Integrating confidentiality measures early can streamline the development process, reducing the need for extensive changes later on and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: Early adoption of confidentiality protocols can help identify and mitigate risks associated with data breaches and other security threats, thereby protecting both the organization and its users.
To effectively integrate confidentiality safeguards, developers should consider the following strategies:
- Incorporate Confidentiality as a Core Requirement: Make confidentiality a fundamental component of the product or service design, not an afterthought.
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involve all relevant stakeholders, including legal, IT security, and end-users, in the early stages of development to ensure comprehensive coverage of confidentiality needs.
- Regular Reviews and Updates: Continuously review and update confidentiality measures to adapt to new threats and regulatory changes.
- Education and Training: Provide ongoing education and training for all team members to ensure they understand the importance of confidentiality and how to implement it effectively.
By understanding and implementing these strategies, organizations can build products and services that not only meet but exceed expectations in terms of confidentiality, thereby fostering a safer and more secure digital environment for all users.
The Importance of Early Privacy Integration
In this section, we delve into the foundational principles that guide the proactive incorporation of confidentiality safeguards in the development process. The emphasis here is on ensuring that these protections are not an afterthought but are woven into the very fabric of the creation process, enhancing the overall security and trustworthiness of the end product.
Proactive Approach: The first principle underscores the need for a proactive stance rather than a reactive one. This means anticipating potential threats to user data and addressing them before they become issues. By integrating confidentiality measures from the outset, developers can prevent many common vulnerabilities that arise when such considerations are added later in the development cycle.
Embedding Confidentiality: Another key aspect is the embedding of confidentiality directly into the architecture of the system. This involves designing systems in such a way that confidentiality is a core component, not a mere add-on. This approach ensures that every part of the system contributes to maintaining user data security, making breaches less likely and more detectable.
Full Lifecycle Protection: Confidentiality must be maintained throughout the entire lifecycle of the product or service. This principle ensures that data protection measures are effective not only at the launch of the product but also as it evolves through updates and maintenance. This continuity of protection is crucial in a world where data threats are constantly evolving.
Visibility and Transparency: Ensuring that the measures taken to protect user data are visible and transparent is another critical principle. Users should be aware of what data is being collected, how it is being used, and what measures are in place to protect it. This transparency builds trust and allows users to make informed decisions about their data.
Respect for User Privacy: Finally, the principle of respect for user privacy is paramount. This involves designing systems that default to protecting user data, rather than requiring users to opt into protection. It also means giving users control over their data and respecting their choices regarding how their data is used and shared.
By adhering to these principles, organizations can build products and services that not only meet regulatory requirements but also foster trust and respect among users, enhancing their overall experience and satisfaction.
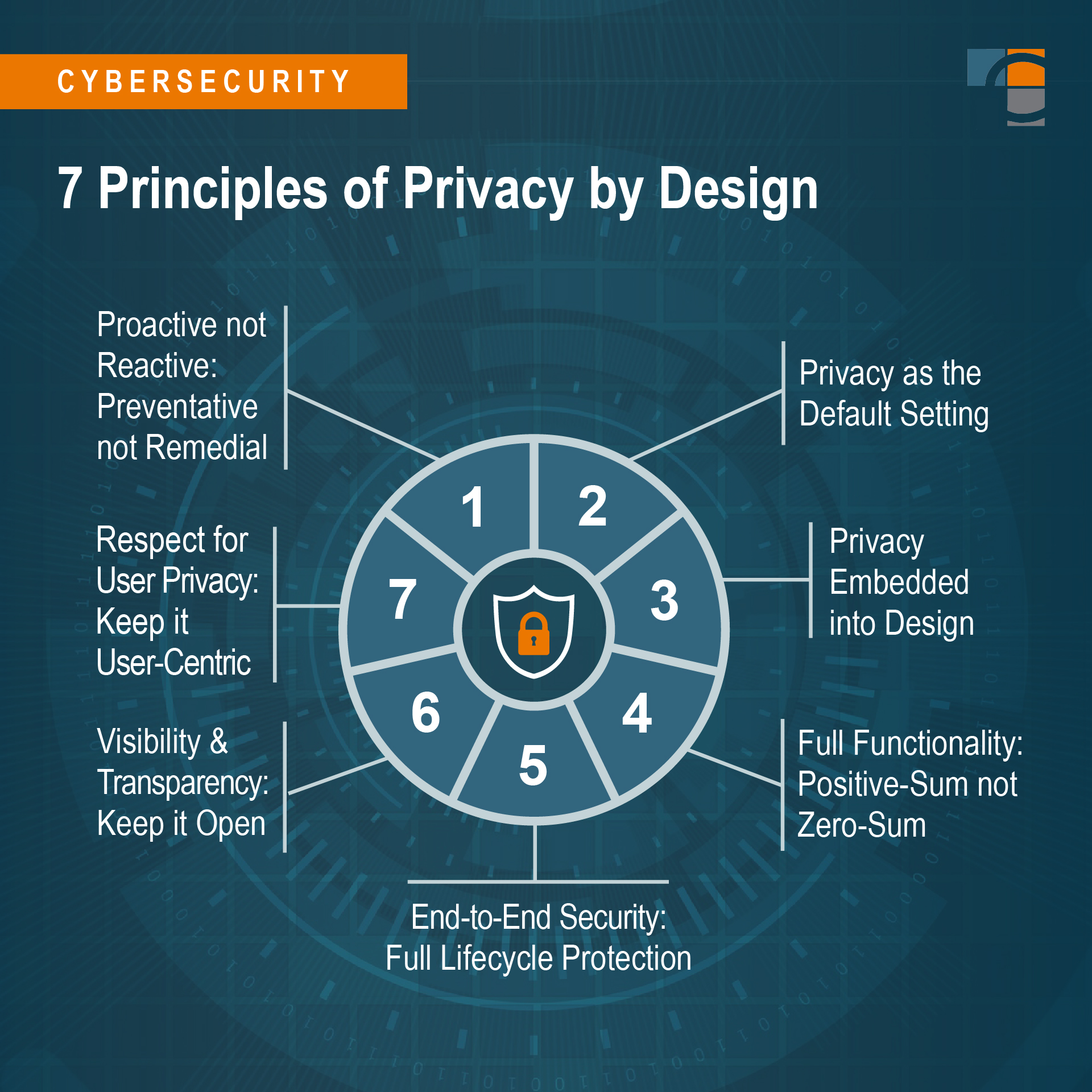
Key Principles of Privacy by Design
This section delves into the foundational practices that guide the integration of confidentiality safeguards within technological advancements. It emphasizes the proactive approach of embedding these protections at the inception of system development, ensuring that user data is respected and secure from the outset.
The first principle involves the proactive rather than reactive approach. This means anticipating potential threats to user data and addressing them before they become issues. It is about preemptive action, rather than waiting for breaches to occur and then reacting to them.
Secondly, the principle of default protection is crucial. This entails configuring systems to protect user information by default, without requiring users to take additional steps. The onus is on the developers to ensure that privacy settings are robust and active as the default state of any application or service.
Thirdly, the principle of full functionality aims to create a positive-sum, not a zero-sum, environment. This means that privacy and utility are not mutually exclusive; both can be enhanced together. The goal is to avoid trade-offs where privacy is compromised for functionality, or vice versa.
The principle of end-to-end security ensures that data is protected throughout its entire lifecycle, from creation to disposal. This comprehensive approach to data integrity and confidentiality ensures that no part of the data handling process is left vulnerable.
Lastly, the principle of visibility and transparency requires that the processes and mechanisms of privacy protection are clear and understandable to users. This openness builds trust and allows users to make informed decisions about their data.
By adhering to these principles, developers can effectively integrate confidentiality safeguards into their projects, fostering a culture of respect for user data within the tech industry.
Implementing Privacy in Software Development
This section delves into the strategic integration of confidentiality safeguards within the software development lifecycle. It emphasizes the proactive measures taken to ensure that user data protection is not an afterthought but is woven into the very fabric of the application from its inception.
To effectively embed confidentiality considerations into software development, several key practices are essential:
- Requirement Analysis: During the initial stages of development, it is crucial to identify and document all potential data handling needs. This includes specifying the types of information that will be collected, how it will be used, and the necessary protections required.
- Design Phase: Incorporate confidentiality into the architecture of the software. This involves designing systems that minimize data collection, use encryption where necessary, and ensure that data storage and processing are secure.
- Implementation: Developers should use secure coding practices and follow industry-standard protocols to protect sensitive information. Regular code reviews and security audits can help identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Testing: Rigorous testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, should be conducted to ensure that the implemented confidentiality measures are effective and robust.
- Deployment and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the software for security breaches and update the system to address new threats. Regularly update privacy policies to reflect any changes in data handling practices.
By following these practices, organizations can ensure that confidentiality is a fundamental aspect of their software products, thereby enhancing trust and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Privacy Considerations in Service Design
This section delves into the critical aspects of incorporating confidentiality safeguards into the blueprint of various offerings. It emphasizes the integration of these protective measures at the foundational stages of development, ensuring that they are not merely an afterthought but a core component of the design process.
When crafting new solutions, it is imperative to consider the legal requirements and ethical standards that govern the handling of personal data. This involves a thorough analysis of the regulatory landscape, which can vary significantly across different jurisdictions. Understanding these frameworks is crucial as they dictate the minimum standards that must be adhered to in order to comply with the law.
Key to this process is the alignment of service features with the principles outlined in various data protection laws. For instance, the concept of data minimization, which advocates for the collection of only the data that is necessary for the specific purpose, should be a guiding principle in the design phase. Similarly, transparency about data usage and the rights of individuals to access, rectify, or delete their data must be integral to the service’s functionality.
Moreover, the design should incorporate mechanisms that facilitate the secure handling of information. This includes implementing robust encryption methods, establishing strict access controls, and regularly auditing data practices to ensure ongoing compliance. By embedding these practices into the service from the outset, organizations can mitigate risks and build trust with their users.
In conclusion, the thoughtful integration of confidentiality considerations into the design of offerings is not only a legal necessity but also a strategic advantage. It demonstrates a commitment to user rights and can differentiate a service in an increasingly privacy-conscious market.
Legal Frameworks Supporting Privacy by Design
This section delves into the critical role that legal structures play in fostering a culture of confidentiality in the development and deployment of digital tools and offerings. By establishing a robust legal foundation, these frameworks not only guide the implementation of protective measures but also ensure compliance with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
In the realm of digital innovation, various legal instruments have been crafted to support the integration of confidentiality safeguards from the inception of product development. These frameworks encompass a range of regulations that mandate the inclusion of data protection features, ensuring that user information is handled responsibly and securely. Key among these are laws that dictate how personal data should be collected, processed, and stored, providing a clear roadmap for developers and service providers.
Moreover, these legal constructs often include provisions for accountability and transparency, requiring entities to demonstrate how they are adhering to confidentiality principles. This not only helps in building trust with users but also serves as a deterrent against potential breaches of data integrity. Compliance with these legal requirements is not just a matter of legality but also of ethical responsibility, reflecting a commitment to safeguarding user privacy.
Additionally, legal frameworks often encourage the adoption of best practices in data management, such as anonymization and encryption, which are integral to maintaining the confidentiality of user information. By setting these standards, the law plays a pivotal role in shaping the technological landscape, ensuring that confidentiality is not an afterthought but a central component of product and service design.
In conclusion, the legal frameworks supporting confidentiality in digital development are essential for fostering an environment where user data protection is prioritized. These structures not only provide the necessary guidelines for compliance but also promote a culture of respect for user privacy, ensuring that confidentiality is embedded in the very fabric of digital innovation.
User Education on Privacy Features

In this section, we delve into the critical role of educating individuals about the protective measures embedded in digital tools. Understanding how these safeguards operate is essential for maximizing their effectiveness and ensuring users feel secure in their digital interactions.
Awareness Campaigns: One of the primary methods for enhancing user knowledge about confidentiality features is through targeted awareness campaigns. These initiatives often include detailed explanations and demonstrations of how to activate and utilize these features effectively.
Interactive Tutorials: Another effective strategy is the creation of interactive tutorials. These guides not only explain but also simulate the use of security settings, allowing users to practice in a controlled environment. This hands-on approach significantly improves retention and application of the learned information.
Feedback Loops: Incorporating feedback loops into the educational process is crucial. By soliciting user experiences and questions, providers can refine their educational materials to better meet the needs and concerns of their audience. This iterative approach ensures that the information remains relevant and accessible.
Collaboration with Educational Institutions: Partnering with schools and universities can extend the reach of privacy education. By integrating these topics into curricula, future generations can grow up with a solid understanding of how to protect your privacy online their digital footprints.
In conclusion, empowering users with knowledge about the protective features of their digital tools is not just beneficial but essential. Through a combination of awareness campaigns, interactive tutorials, feedback mechanisms, and educational partnerships, we can foster a more informed and secure digital community.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of Data Protection by Default
This section delves into real-world examples where the principle of embedding data protection measures from the outset has been effectively applied. By examining these instances, we can gain valuable insights into how organizations have navigated the complexities of integrating robust data security practices into their core operations.
- Healthcare Application: A leading healthcare provider implemented a system where patient information was automatically encrypted at the point of entry. This ensured that sensitive data was protected from the moment it was collected, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Financial Services Platform: A major banking app incorporated biometric authentication as a default feature. This not only enhanced user convenience but also strengthened the security of financial transactions, aligning with regulatory requirements for data protection.
- Educational Software: An educational platform designed for children integrated strict access controls and data minimization practices. This approach safeguarded student data and complied with stringent privacy laws governing the protection of minors’ information.
- E-commerce Website: A popular online retailer implemented a feature that anonymized customer data by default, stripping out identifiable information before storing it. This practice significantly reduced the risk of data breaches and demonstrated a commitment to customer privacy.
These case studies highlight the practical benefits of adopting a proactive approach to data security. By embedding protective measures at the core of their systems, these organizations have not only enhanced their security posture but also fostered trust among their users.
- Enhanced User Trust: By prioritizing data security, these companies have built a reputation for reliability and trustworthiness, which is crucial in maintaining customer loyalty.
- Compliance with Regulations: The proactive integration of data protection measures helps these entities meet stringent regulatory requirements, avoiding costly penalties and legal issues.
- Operational Efficiency: Implementing data security from the beginning reduces the need for costly retrofits and minimizes disruptions to business operations.
In conclusion, the examples provided illustrate the tangible advantages of incorporating data protection measures by default. These successful implementations serve as a blueprint for other organizations looking to enhance their data security practices and comply with evolving privacy regulations.
Challenges in Adopting Privacy by Design

This section delves into the complexities and obstacles faced when integrating data protection principles at the core of technological and operational frameworks. Despite the growing awareness and necessity for safeguarding personal information, the implementation of such measures presents significant challenges. These hurdles range from technical and organizational to legal and cultural, influencing the effectiveness and adoption rates of these practices.
One of the primary challenges is the technical complexity involved in embedding data protection features into existing systems. Developers often encounter difficulties in retrofitting these features without disrupting the functionality of the systems. Additionally, the rapid evolution of technology necessitates continuous updates and adaptations, which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming.
Organizational resistance is another significant barrier. Many entities are hesitant to overhaul their existing processes due to the perceived high costs and potential disruption to business operations. There is also a lack of comprehensive understanding among stakeholders about the long-term benefits of proactive data protection measures, which can lead to underinvestment in these areas.
Legal and regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity. With varying and sometimes conflicting regulations across different jurisdictions, ensuring compliance can be a daunting task. This is further complicated by the dynamic nature of legal frameworks, which require constant monitoring and adjustments to maintain compliance.
Cultural and educational challenges also play a role. There is a need for widespread education and awareness about the importance of safeguarding personal data. Users often lack the knowledge to make informed decisions about their data privacy, and businesses may not fully appreciate the value of data protection in building consumer trust and loyalty.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Complexity | Difficulty in integrating data protection features into existing systems without affecting functionality. |
| Organizational Resistance | Hesitance to change existing processes due to cost and operational disruption concerns. |
| Legal Compliance | Complexity in adhering to varying and evolving legal requirements across different regions. |
| Cultural and Educational Gaps | Lack of awareness and understanding about the importance of data protection among users and businesses. |
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including technological innovation, organizational commitment, legal harmonization, and educational initiatives. As we look to the future, it is crucial to continue exploring and implementing strategies that facilitate the seamless integration of data protection principles into all facets of technology and service development.
Future Trends in Privacy by Design
As we advance into the digital era, the integration of confidentiality safeguards within technological frameworks is poised to evolve significantly. This section explores the forthcoming shifts in how organizations approach the embedding of data protection measures in their operational structures, ensuring a proactive stance rather than a reactive one.
The trajectory of incorporating confidentiality measures is influenced by several key factors:
- Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): These technologies are expected to play a crucial role in enhancing the detection and prevention of unauthorized data access, thereby fortifying confidentiality protocols.
- Increased Regulatory Compliance: With the growing complexity of global data protection laws, there will be a heightened focus on compliance, driving organizations to adopt more robust confidentiality frameworks.
- Shift Towards Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): The development and adoption of PETs will become more prevalent, offering innovative solutions to protect sensitive information without compromising functionality.
- User Empowerment: There will be a greater emphasis on educating users about their rights and the tools available to manage their personal information, fostering a more informed and empowered user base.
- Cross-Industry Collaboration: The sharing of best practices and collaborative efforts across different sectors will lead to more comprehensive and effective confidentiality strategies.
Moreover, the future may witness the following specific trends:
- Customized Confidentiality Settings: Personalized data protection settings tailored to individual user preferences and behaviors will become more common.
- Real-time Data Protection: Continuous monitoring and real-time intervention to safeguard data will be a standard feature in future technological solutions.
- Ethical Considerations in Data Handling: The ethical implications of data usage will gain prominence, influencing the design and implementation of confidentiality measures.
- Integration of Confidentiality in IoT Devices: As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, ensuring the security of connected devices will be paramount, leading to more stringent confidentiality protocols in their design.
In conclusion, the future of embedding confidentiality safeguards within technological and operational frameworks is bright, with a clear shift towards proactive and user-centric approaches. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the strategies and tools used to protect sensitive information, ensuring a balance between functionality and security.




0 Comments
You must be logged in to post a comment.